Top 10 Types of Electrical Cables You Need to Know for Your Projects
In the world of construction and electrical installations, understanding the different types of electrical cables is crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and compliance with regulations. Renowned electrical engineer, John Smith, emphasizes the importance of this knowledge, stating, "Choosing the right electrical cable can be the difference between a successful project and potential hazards." With numerous options available on the market, each designed to serve specific purposes, it can be daunting for contractors, electricians, and DIY enthusiasts to navigate through them.
This article aims to illuminate the top 10 types of electrical cables that are essential for various projects. From power distribution to telecommunications, the right electrical cable plays a pivotal role in the overall functionality and safety of electrical systems. Understanding the characteristics and applications of these cables will not only aid in making informed decisions but also enhance the quality and durability of installations. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting, being equipped with knowledge about electrical cables can greatly impact your project's outcome and ensure adherence to industry standards.

Types of Electrical Cables: Overview and Industry Standards
When it comes to electrical cables, understanding the various types and their corresponding industry standards is crucial for any project. Different applications require specific cable types to ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance with regulations. For instance, there are non-metallic sheathed cables commonly used in residential wiring, which feature excellent insulation properties. In contrast, armored cables are designed for more hazardous environments, providing additional protection against physical damage. Each type serves a unique purpose, catering to the needs of different electrical systems and installations.
Moreover, industry standards play a significant role in determining the specifications for electrical cables. Organizations such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States outline essential guidelines to ensure that cables meet safety and performance criteria. Additionally, international standards like those set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) provide a framework for quality and compatibility globally. Understanding these regulations is vital for selecting the right cables, as it helps avoid potential hazards and ensures that projects are executed smoothly and within legal requirements.
Understanding Voltage Ratings and Their Importance in Cable Selection
When selecting electrical cables for projects, understanding voltage ratings is crucial. Voltage ratings indicate the maximum amount of voltage that a cable can safely carry without the risk of electrical breakdown. According to industry reports from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), proper voltage rating selection is essential to prevent overheating, reduce the risk of short circuits, and enhance overall safety. For instance, cables rated for 600V are typically used in residential applications, while those with ratings of 1kV and above are essential for industrial uses, where higher voltage levels are common.
The importance of adhering to voltage ratings cannot be overstated. Utilizing cables with insufficient voltage ratings increases the likelihood of insulation failure, which can lead to significant hazards such as electrical fires or equipment damage. A 2022 study published by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) highlights that improper cable selection, predominantly due to neglecting voltage ratings, contributes to approximately 30% of electrical failures in commercial settings. Thus, understanding and applying the correct voltage ratings not only ensures compliance with safety regulations but also enhances the longevity and reliability of the electrical systems integral to various projects.
Top 10 Types of Electrical Cables You Need to Know for Your Projects
| Cable Type | Voltage Rating | Common Uses | Wire Material |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVC Insulated Cable | 600V | Residential Wiring | Copper |
| XLPE Insulated Cable | 1kV - 33kV | Industrial Applications | Aluminum |
| Armoured Cable | 600V | Outdoor Applications | Copper |
| Telecommunication Cable | Various | Data Transmission | Copper/Fiber |
| H05VV-F Cable | 300V | Flexible Equipment | Copper |
| RVS Cable | 450V | Home Appliances | Copper |
| SCT Cable | 300V | Lighting | Copper |
| PV Solar Cable | 1000V | Solar Power Systems | Copper |
| Silicone Rubber Cable | 600V | High Temperature Applications | Copper |
| Grounding Cable | 600V | Electrical Grounding | Copper |
Comparative Analysis of Copper vs. Aluminum Wiring in Electrical Applications

When considering electrical wiring for your projects, one of the key debates revolves around the choice between copper and aluminum. Copper wiring has long been favored for its superior conductivity and durability. It offers lower electrical resistance, which translates to less energy loss and improved efficiency. Additionally, copper is less prone to oxidation, making it a reliable choice in environments where moisture is a concern.
On the other hand, aluminum wiring presents a more cost-effective alternative. While its conductivity is lower than copper, advancements in technology have made aluminum wiring more effective than ever. Its lightweight nature makes it easier to handle and install, particularly for large or complex projects. However, it's crucial to note that aluminum can be more susceptible to expansion and contraction, which may lead to connection issues over time.
Tips for selecting the appropriate wiring for your project include assessing the specific electrical load requirements, environment factors, and budget constraints. Always ensure that the wiring is compatible with the intended application. Additionally, consider consulting with a professional electrician to analyze the long-term performance benefits of copper versus aluminum in your particular context. Remember, the right choice can significantly impact the safety and efficiency of your electrical system.
Key Features of Low-Voltage vs. High-Voltage Electrical Cables
When undertaking electrical projects, understanding the differences between low-voltage and high-voltage electrical cables is essential. Low-voltage cables typically operate at voltages up to 1,000 volts and are primarily used for applications like residential wiring, lighting systems, and signal transmissions. These cables are designed with insulation that can withstand lower electrical stresses, making them suitable for safe, efficient energy distribution in everyday use. Their flexibility and lightweight nature allow for easier installation, especially in tight spaces or intricate configurations.
In contrast, high-voltage cables are designed for applications involving higher electrical potentials, generally exceeding 1,000 volts. These cables are constructed with robust insulation materials and reinforced conductors to endure the extreme conditions associated with high-voltage transmission. They are often used in utility-scale power distribution and industrial settings, where the risk of electrical faults is heightened. The thicker insulation and specialized design of high-voltage cables help prevent dielectric breakdown and maintain safety in demanding environments.
Understanding these key features is crucial for ensuring that the right type of cable is used for the intended application, providing both safety and efficiency throughout any project.
Common Electrical Cable Applications and Their Specific Requirements
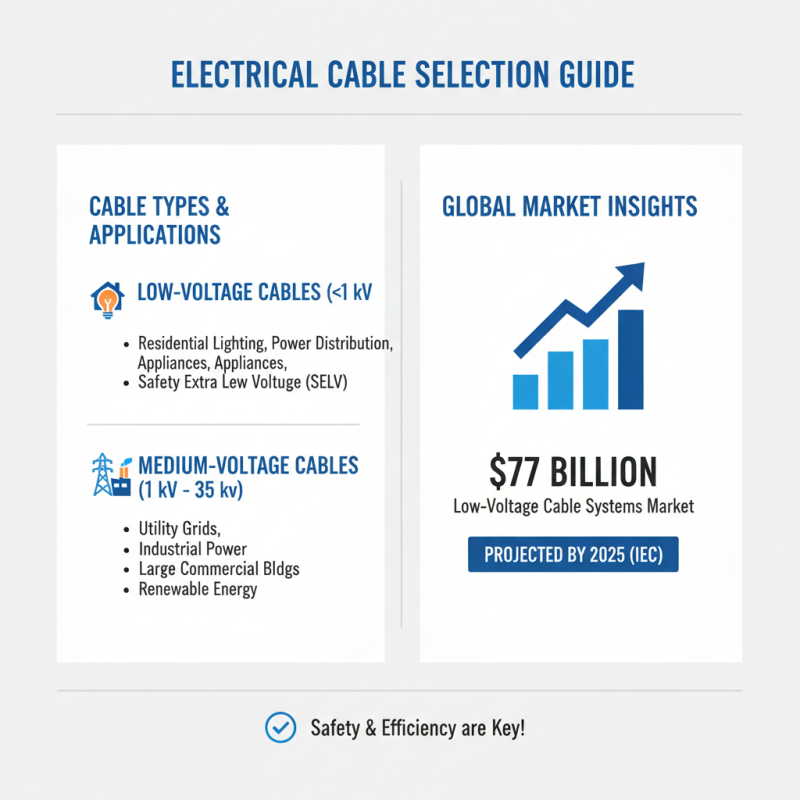
When selecting electrical cables for your projects, understanding the specific applications and requirements is essential. Different types of electrical cables serve distinct purposes, and knowing these can enhance both safety and efficiency in your installations. For instance, low-voltage cables are often used in residential settings for lighting and power distribution, while medium-voltage cables are crucial for utility applications, with a typical voltage range of 1 kV to 35 kV. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission, the global market for low-voltage cable systems is projected to reach approximately $77 billion by 2025, emphasizing the growing demand for reliable electrical infrastructures.
Moreover, specialized cables such as armored cables are designed to protect against physical damage in industrial environments, while fiber optic cables are essential for high-speed data transmission. Industry reports indicate that the fiber optic cable market is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 10% from 2020 to 2027, driven by rising demand for high-bandwidth applications. Each type of cable comes with specific requirements regarding installation practices, environmental considerations, and adherence to safety standards, making it crucial for professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike to evaluate their project needs carefully. Understanding these specifications can prevent costly mistakes and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
Related Posts
-

The Comprehensive Ultimate Guide to Understanding Electrical Cable Selection and Installation
-

10 Compelling Reasons Why Cable Wire is Essential for Your Global Sourcing Needs
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Outdoor Extension Cord for Your Needs
-

5 Reasons Why Wire EDM is the Best Choice for Precision Manufacturing in 2023
-
Top Power Cords for Home and Office Essential Guide to Choosing the Best
-

What are Electrical Wire Connectors? Exploring Their Types, Uses, and Market Trends in 2023